Apache APISIX builds upon the OpenResty reverse-proxy to offer a plugin-based architecture. The main benefit of such an architecture is that it brings structure to the configuration of routes. It's a help at scale, when managing hundreds or thousands of routes.
In this post, I'd like to describe how plugins, priority, and phases play together and what pitfalls you must be aware of.
APISIX plugin's priority
When you configure a route with multiple plugins, Apache APISIX needs to execute them in a consistent order so that the results are the same over time. For this reason, every APISIX plugin has a harcoded priority. You can check a plugin priority directly in the code. For example, here's the relevant code fragment for the basic-auth plugin:
local _M = {
version = 0.1,
priority = 2520, #1
type = 'auth',
name = plugin_name,
schema = schema,
consumer_schema = consumer_schema
}
- Priority is 2520
For documentation purposes, the default-config.yaml file lists the priority of all out-of-the-box plugins. Here's an excerpt:
plugins:
- ldap-auth # priority: 2540
- hmac-auth # priority: 2530
- basic-auth # priority: 2520
- jwt-auth # priority: 2510
- key-auth # priority: 2500
- consumer-restriction # priority: 2400
- forward-auth # priority: 2002
- opa # priority: 2001
- authz-keycloak # priority: 2000
#- error-log-logger # priority: 1091
- proxy-cache # priority: 1085
- body-transformer # priority: 1080
- proxy-mirror # priority: 1010
- proxy-rewrite # priority: 1008
- workflow # priority: 1006
- api-breaker # priority: 1005
- limit-conn # priority: 1003
- limit-count # priority: 1002
- limit-req # priority: 1001
Imagine a route configured with proxy-mirror and proxy-rewrite. Because of their respective priority, proxy-mirror would run before proxy-rewrite.
upstream:
- id: 1
nodes:
"oldapi:8081": 1
routes:
- id: 1
uri: "/v1/hello*"
upstream_id: 1
plugins:
proxy-rewrite: #1-3
regex_uri: ["/v1(.*)", "$1"]
proxy-mirror: #2
host: http://new.api:8082
- The plugin ordering in this file is not relevant
proxy-mirrorhas priority 1010 and will execute firstproxy-rewritehas priority 1008 and will run second
The above setup has an issue. For example, if we call localhost:9080/v1/hello, APISIX will first mirror the request, then remove the /v1 prefix. Hence, the new API receives /v1/hello instead of /hello. It's possible to override the default priority to fix it:
routes:
- id: 1
uri: "/v1/hello*"
upstream_id: 1
plugins:
proxy-rewrite:
_meta:
priority: 1020 #1
regex_uri: ["/v1(.*)", "$1"]
proxy-mirror:
host: http://new.api:8082
- Override the default priority
Now, proxy-rewrite has higher priority than proxy-mirror: the former runs before the latter.
In this case, it works flawlessly; in others, it might not. Let's dive further.
APISIX phases
APISIX runs plugins not only according to their priorities but also through dedicated phases. Because APISIX builds upon OpenResty, which builds upon ngxinx, the phases are very similar to the phases of these two components.
nginx defines several phases an HTTP request goes through:
NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASENGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASENGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASENGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASENGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASENGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASENGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASENGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASENGX_HTTP_PRECONTENT_PHASENGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASENGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE
Each phase focuses on a task, i.e., NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE verifies that the client is authorized to make the request.
In turn, OpenResty offers similarly named phases.

image:77d1c09e-1a37-11e6-97ef-d9767035fc3e.png[,840,761]
Finally, here are the phases of Apache APISIX:
rewriteaccessbefore_proxyheader_filterbody_filterlog
From Apache APISIX documentation:
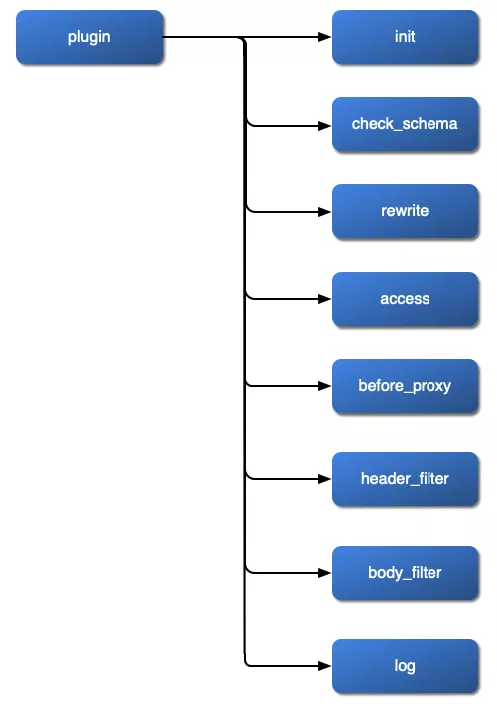
We have seen two ways to order plugins: by priority and by phase. Now comes the most important rule: order by priority only works inside a phase!
For example, the redirect plugin has a priority of 900 and runs in phase rewrite; the gzip plugin has a priority of 995 and runs in phase body_filter. Regardless of their respective priorities, redirect will happen before gzip, because rewrite happens before body_filter. Likewise, changing a priority won't "move" a plugin out of its phase.
The example above with proxy-mirror and proxy-rewrite worked because both run in the rewrite phase.
The main issue is that priority is documented in the config-default.yaml file, while the phase is buried in the code. Worse, some plugins run across different phases. For example, let's check the proxy proxy-rewrite plugin and, more precisely, the functions defined there:
local function is_new_headers_conf(headers)local function check_set_headers(headers)function _M.check_schema(conf)function _M.rewrite(conf, ctx)
The name of the rewrite() function is suspiciously similar to one of the phases above. Looking at other plugins, we see the same pattern repeat. Apache APISIX runs plugin functions with the same name as the phase.
I took the liberty of summarizing all plugins and their respective phases in a table.
| Plugin | Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
redirect | X | |||||
echo | X | X | ||||
gzip | X | |||||
real-ip | X | |||||
ext-plugin-pre-req | X | |||||
ext-plugin-post-req | X | |||||
ext-plugin-post-resp | X | |||||
workflow | X | |||||
| Transformation | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
response-rewrite | X | X | ||||
proxy-rewrite | X | |||||
grpc-transcode | X | X | X | |||
grpc-web | X | X | X | |||
fault-injection | X | |||||
mocking | X | |||||
degraphql | X | |||||
body-transformer | X | X | X | |||
| Authentication | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
key-auth | X | |||||
jwt-auth | X | |||||
basic-auth | X | |||||
authz-keycloak | X | |||||
authz-casdoor | X | |||||
wolf-rbac | X | |||||
openid-connect | X | |||||
cas-auth | X | |||||
hmac-auth | X | |||||
authz-casbin | X | |||||
ldap-auth | X | |||||
opa | X | |||||
forward-auth | X | |||||
| Security | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
cors | X | X | ||||
uri-blocker | X | |||||
ua-restriction | X | |||||
referer-restriction | X | |||||
consumer-restriction | X | |||||
csrf | X | X | ||||
public-api | X | |||||
chaitin-waf | X | |||||
| Traffic | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
limit-req | X | |||||
limit-conn | X | X | ||||
limit-count | X | |||||
proxy-cache (init) | X | X | X | |||
proxy-cache (disk) | X | X | ||||
proxy-cache (memory) | X | X | X | |||
request-validation | X | |||||
proxy-mirror | X | |||||
api-breaker | X | X | ||||
traffic-split | X | |||||
request-id | X | X | ||||
proxy-control | X | |||||
client-control | X | |||||
| Observability | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
zipkin | X | X | X | X | ||
skywalking | X | X | ||||
opentelemetry | X | X | ||||
prometheus | ||||||
node-status | ||||||
datadog | X | |||||
http-logger | X | X | ||||
skywalking-logger | X | |||||
tcp-logger | X | |||||
kafka-logger | X | X | ||||
rocketmq-logger | X | X | ||||
udp-logger | X | |||||
clickhouse-logger | X | X | ||||
syslog | X | |||||
log-rotate | ||||||
error-log-logger | ||||||
sls-logger | X | |||||
google-cloud-logging | X | |||||
splunk-hec-logging | X | |||||
file-logger | X | X | ||||
loggly | X | X | ||||
elasticsearch-logger | X | |||||
tencent-cloud-cls | X | X | X | |||
loki-logger | X | X | ||||
| Other | rewrite | access | before_proxy | header_filter | body_filter | log |
serverless | X | |||||
openwhisk | X | |||||
dubbo-proxy | X | |||||
kafka-proxy | X | |||||
Conclusion
I've detailed Apache APISIX plugin phases and priorities in this post. I've explained their relationship with one another. Icing on the cake, I documented each out-of-the-box plugin's phase(s). I hope it will prove helpful.
To go further:
Originally published at A Java Geek on December 10th, 2023
