In this article, you can understand how iQIYI's technical team updates and integrates the company structure based on Apache APISIX gateway to create a brand-new gateway service.
Background
iQIYI has developed a gateway-skywalker, it is based on the secondary development of Kong, the current traffic is also relatively large, the daily peak of the gateway stock business million QPS, the number of API routes tens of thousands. But the product’s shortcomings began to show up in the wake of its use.
- Performance is not satisfactory, because the volume of business, every day received a lot of CPU IDLE too low alert
- The components of the system architecture depend on many
- The development cost of operation and maintenance is high
After taking over the project this year, we started to do some research on gateway products in the light of the problems and dilemmas mentioned above, and then we found Apache APISIX.
Apache APISIX Advantage
Before choosing Apache APISIX, the iqiyi platform was already using Kong, but it was later abandoned.
Why Give Up Kong
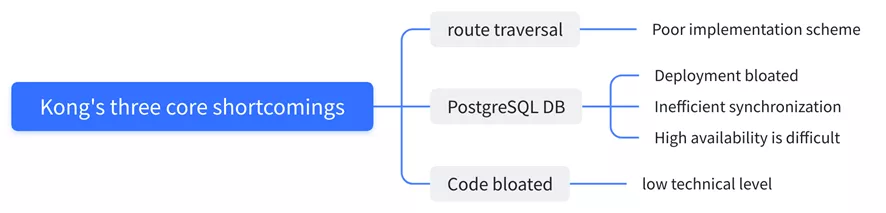
Kong uses PostgreSQL to store its information, which is obviously not a good way. We also looked at the performance of Apache APISIX compared to Kong in the course of our research, and it’s amazing that Apache Apisix is 10 times better than Kong in terms of performance optimization. We also compared some of the major gateway products, Apache APISIX’s response latency is more than 50% lower than other gateways, and Apache APISIX can still run stably when the CPU reaches more than 70% .
We also found out that Apache APISIX, like Kong, is based on the OpenResty technology, so the cost of technology migration is relatively low. And Apache APISIX is very adaptable and can be easily deployed in a variety of environments, including cloud computing platforms.
We also saw that Apache APISIX was very active throughout the open source project, handled the issues very quickly, and the cloud native architecture of the project was in line with our follow up plans, so we chose Apache APISIX.
Architecture Based on Apache APISIX
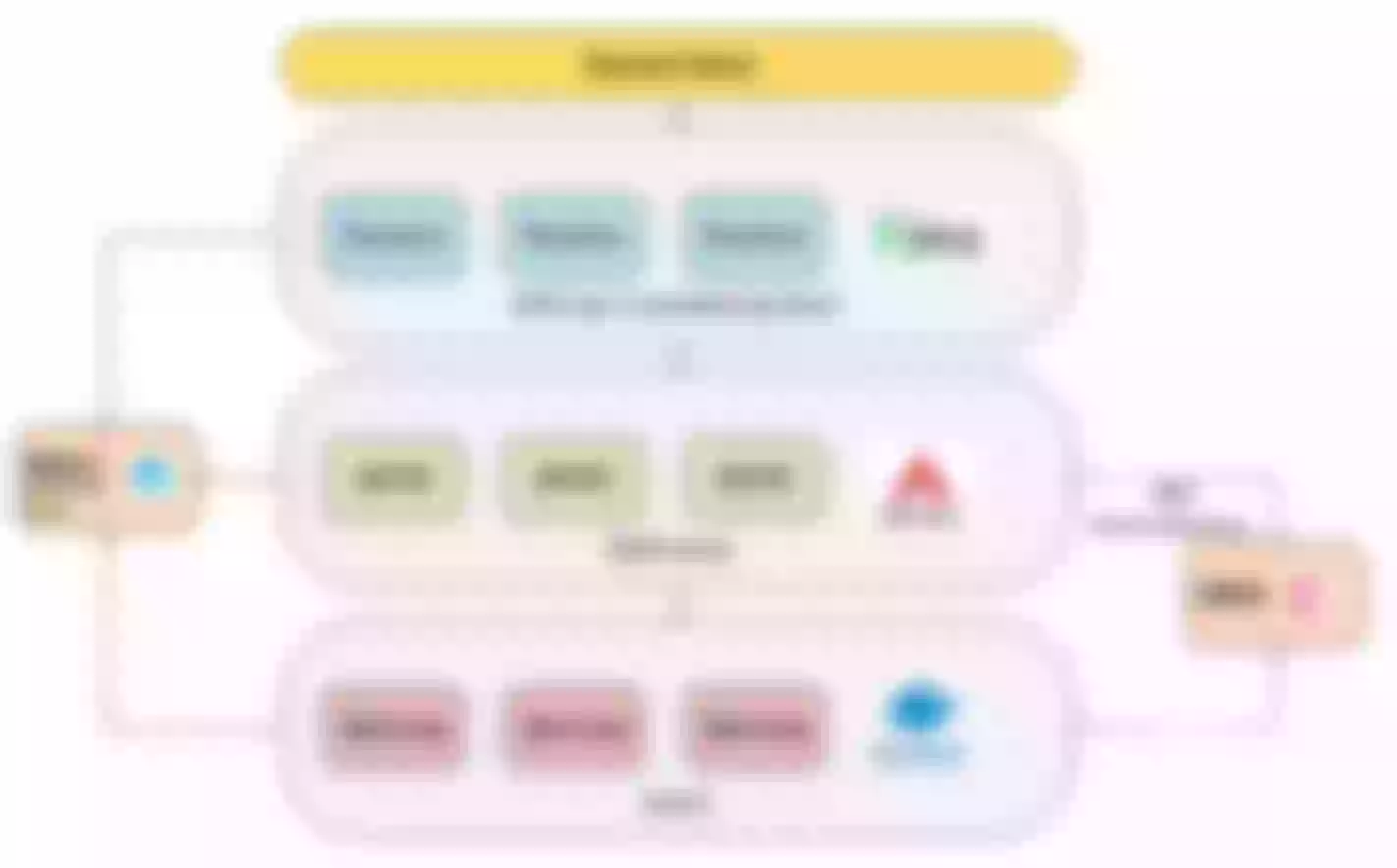
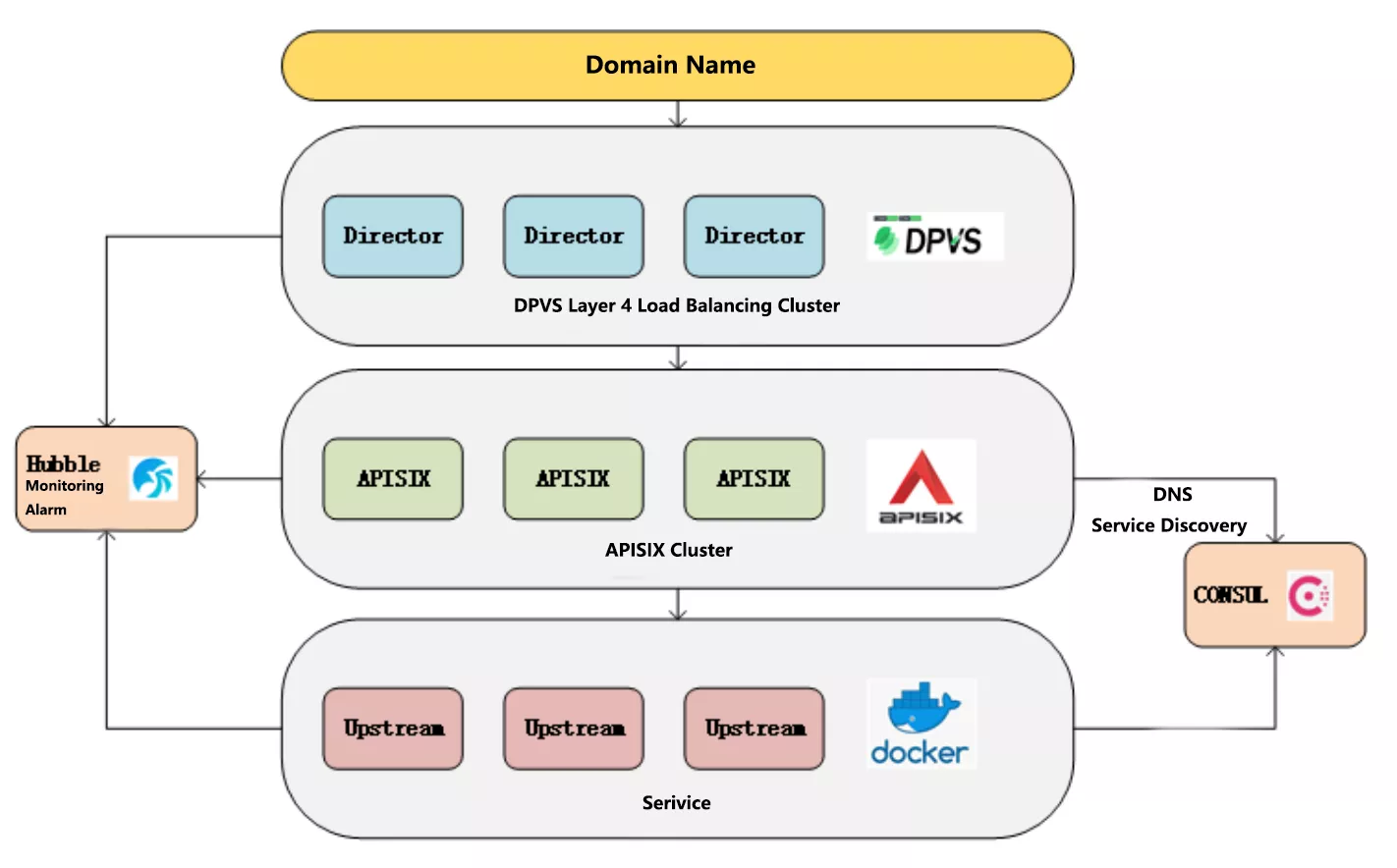
The overall architecture of iQIYI Gateway is shown below, including domain name, gateway to service instance and monitoring alarm. DPVS is an open source project within the company based on LVS, Hubble monitoring alerts is also a deep secondary development based on an open source project, and the Consul area has been optimized for performance and high availability.
Scenario 1: Microservice Gateway
About the gateway this piece, simple from the control surface and the data surface introduce.
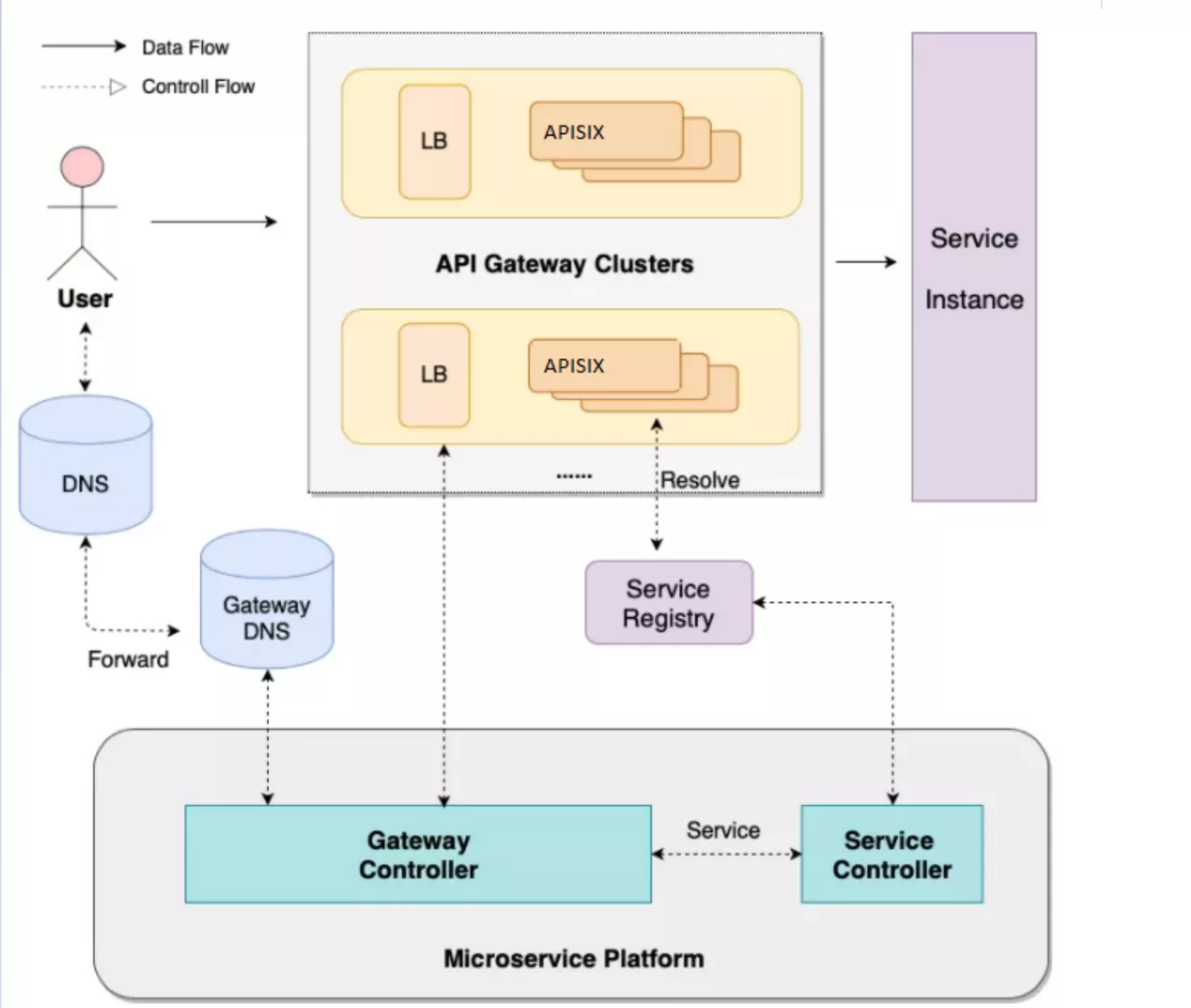
The data plane is mainly oriented to the front-end users, and the whole architecture from LB to Gateway is multi-location and multi-link disaster deployment.
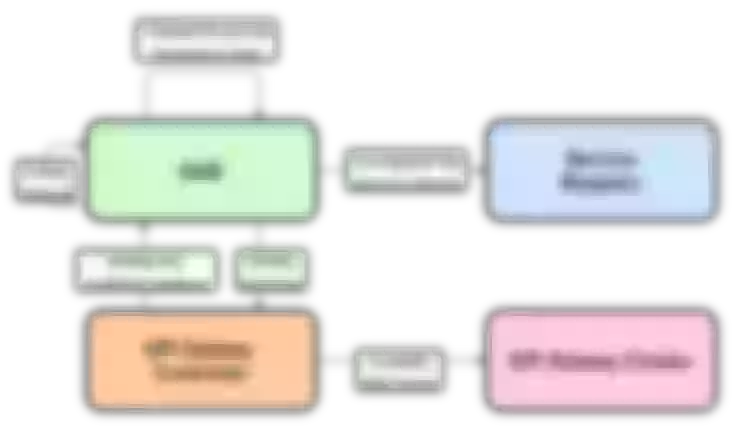
From the perspective of control surface, because of the multi-cluster composition, there will be a micro-service platform to do cluster management and service management. Microservice platforms allow users to experience services as one-stop-shops that expose them to immediate use without having to submit a work order. The back end of the control panel will have Gateway Controller, which controls the creation of all apis, plug-ins, and related configurations, and Service Controller, which controls Service registration and health checks.
Scenario 2: Basic Functions
At present, the API architecture based on Apache APISIX has realized some basic functions, such as current limiting, authentication, alarm, monitoring and so on.
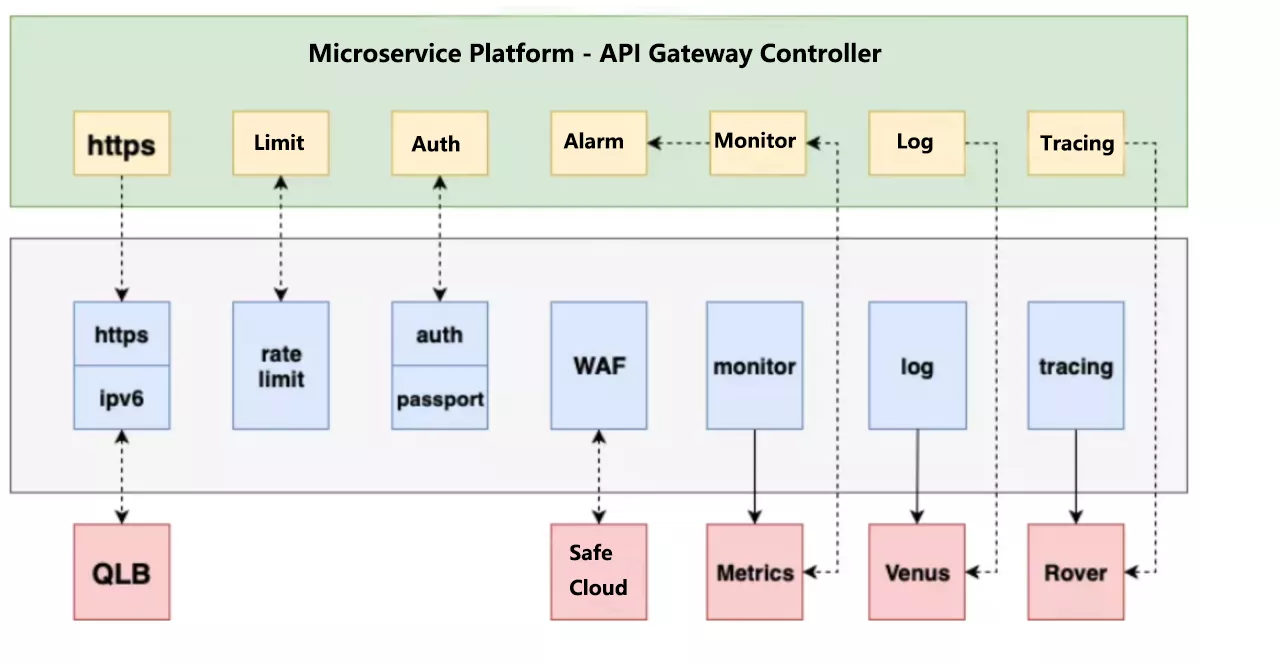
First is the HTTPS section, iQIYI for security reasons, certificates and keys are not stored on the gateway machine, will be placed on a dedicated remote server. We didn’t support this when we used Kong, we used the prefix Nginx to do HTTPS Offload, and after the migration to Apache APISIX, we implemented this feature on Apache APISIX, which is a layer less forwarding over the link.
In the current limiting function, in addition to the basic current limiting, but also added a precise current limiting and user-specific granularity of the current limiting. Authentication function, in addition to the basic API Key authentication, for specialized services also provide the relevant Passport authentication. For black product filtering, access to the company’s WAF Security Cloud.
The monitoring feature is currently implemented using the Apache APISIX plug-in Prometheus, and the metrics data will interface directly with the company’s monitoring system. Logging and call chain analysis is also supported through Apache APISIX.
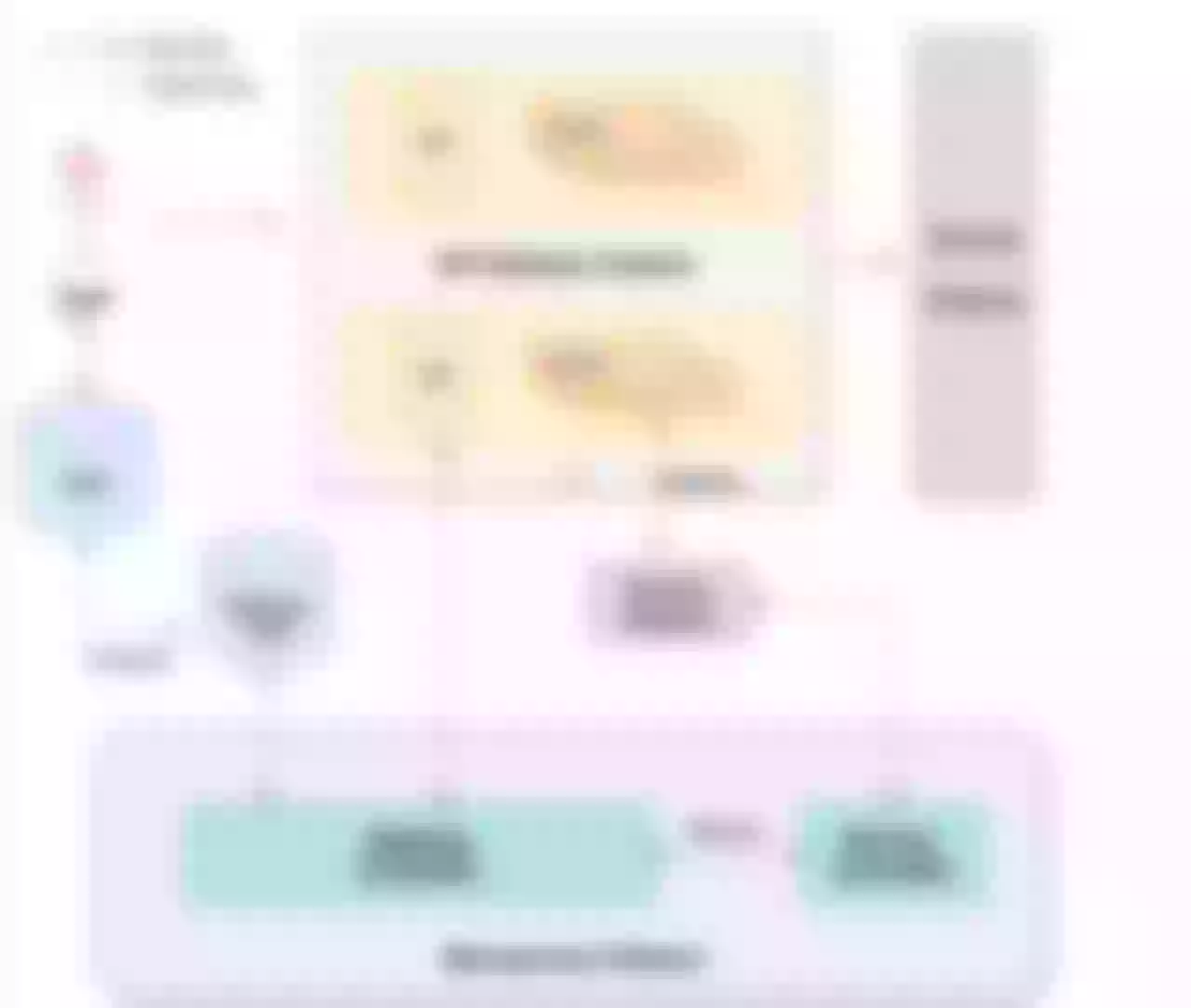
Scenario 3: Serviece Discovery
With regard to the above-mentioned service discovery, it is mainly through the service center to register the service to the Consul cluster, and then through the DNS service discovery to do dynamic updates, qae is a micro-service platform in our company. A simple example illustrates the general flow of updating a backend application instance.
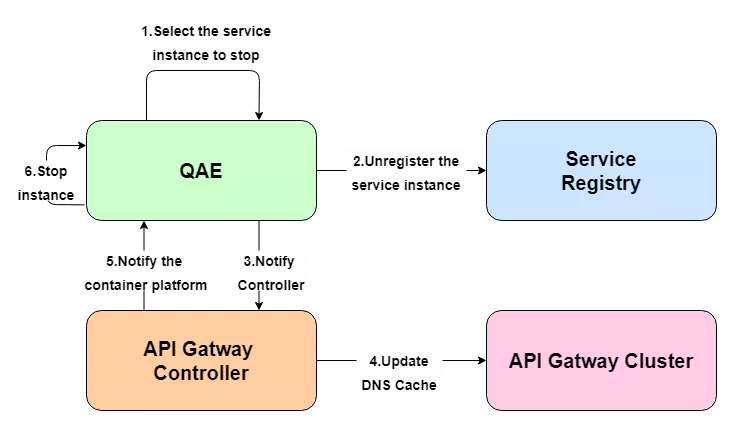
When the instance changes, the corresponding node is first unlogged from Consul and a request to update the DNS cache is sent to the gateway through the API Gateway Controller. After the cache update is successful, the Controller then feeds back to the QAE platform to stop the associated back-end application node and avoid reforwarding traffic to the offline node.
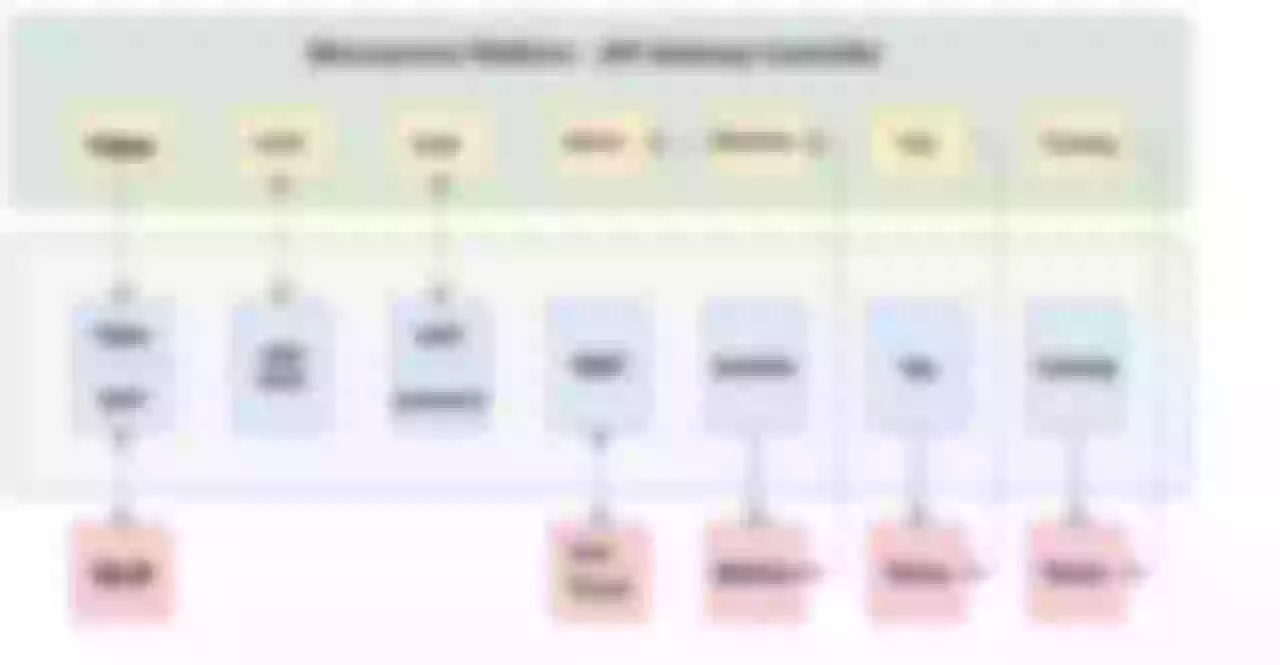
Scenario 4: Directional Route
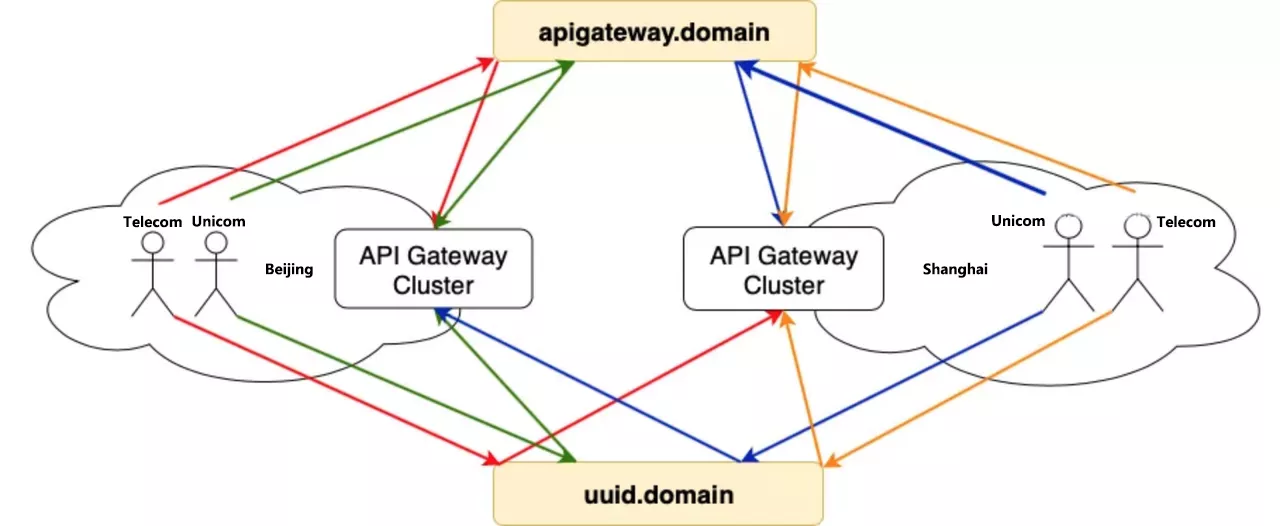
The gateway is multi-location deployment, build a set of multi-location backup link in advance, at the same time suggest the user back-end service is also multi-location deployment nearby. Then the user creates an API service on the Skywalker Gateway platform, the Controller deploys the API routing on the entire DC gateway cluster, and the business domain defaults to CNAME on the unified gateway domain name.
It provides multi-local access, disaster preparedness and handoff capability for business directly, and also supports user-defined resolution routing. For the user’s own fault-cut flow, blue-green deployment, canary release needs, users can use the uuid domain name to customize the resolution of routing configuration, but also to support the back-end service discovery custom scheduling.
Scenario 5: Multi-site Multi-level Disaster Tolerance
As we mentioned earlier, at the business level we have business proximity and disaster preparedness requirements for large volumes of traffic, large clusters, and a wide audience of clients.
For disaster preparedness, in addition to multi-link backup, but also consider multi-level multi-node problem, fault node closer to the client, the greater the impact of business and traffic.
- If it is the farthest back-end service node failure, depending on the health check mechanism of the gateway and the service center, it can realize the fuse of the fault single node or the switch of the fault DC, and the influence scope is limited to the specified service, the user is not aware.
- If it is a gateway level fault, we need to rely on the health check mechanism of L4 DPVS, fusing the fault gateway node, the influence range is small, the user is not aware.
- If the fault points can not be repaired by the above-mentioned fusing measures, it is necessary to rely on the multi-point availability dialing of the domain name granularity to realize the automatic fault switching at the domain name resolution level, which is a relatively slow way to repair the fault, affect the business much, the user can feel.
Problems Encountered during Migration
During our migration practice from Kong to Apache APISIX, we addressed and optimized some known architectural issues, but also encountered some new ones.
Result 1: SNI Compatibility Issues Not Supported in The Front End Were Resolved
Most of the frontend is now supported for SNI, but you’ll also encounter a few frontend that won’t pass the hostname during SSL. At present, we have done a compatibility for this situation, using port matching method to obtain the relevant certificates.
Result 2: A Large Number of API Routing Matching Problems Have Been Optimized
As I said before, we currently have more than 9,000 API services running directly online, and may increase in the future. In order to solve this problem, we made some performance optimization, according to the API to decide whether to match the domain name or the path first.
Result 3: The Limitation of ETCD Interface Is Solved
After accessing Apache APISIX, the ETCD interface limitation has also been resolved and the 4M limit has now been lifted.
Result 4: Performance Issues Optimized for The Number of ETCD Connections
Currently, every worker at Apache APISIX is connected to the ETCD, and every listening directory is going to make a connection. For example, a physical machine is 80core, with 10 listening directories and 800 connections on a single gateway server. With a gateway cluster of 10,8,000 connections is a lot of pressure on the ETCD. The optimization is to take one worker and listen to a limited set of necessary directories and share the information with the rest of the workers.
To Be Optimized
In addition to the above problems, there are also a number of issues are being optimized.
- A number of API issues, even if APISIX is supported, we need to consider other component-dependent bottlenecks. Such as the ETCD, Prometheus Monitoring and logging services described above. So in the future, we may adopt the two ways of large cluster sharing and small cluster independence to mix the deployment of business, for example, some important business we will deploy in small clusters.
- With respect to the Prometheus monitoring metric, we will continue to scale down and optimize the DNS service to find more.
Expectations for Apache APISIX
We hope that in future development updates Apache APISIX will not only support more functionality, but also maintain performance efficiency and stability over time.