This article shows the procedure of installing and deploying Apache APISIX and Apache APISIX Ingress Controller in the Rancher App Store (Catalog), and how to proxy Kubernetes services through them.
Prerequisite
Existing Kubernetes clusters are all hosted on Rancher.
Step 1: Configure Helm Chart in Rancher
Visit Rancher’s Tools — Catalogs page.
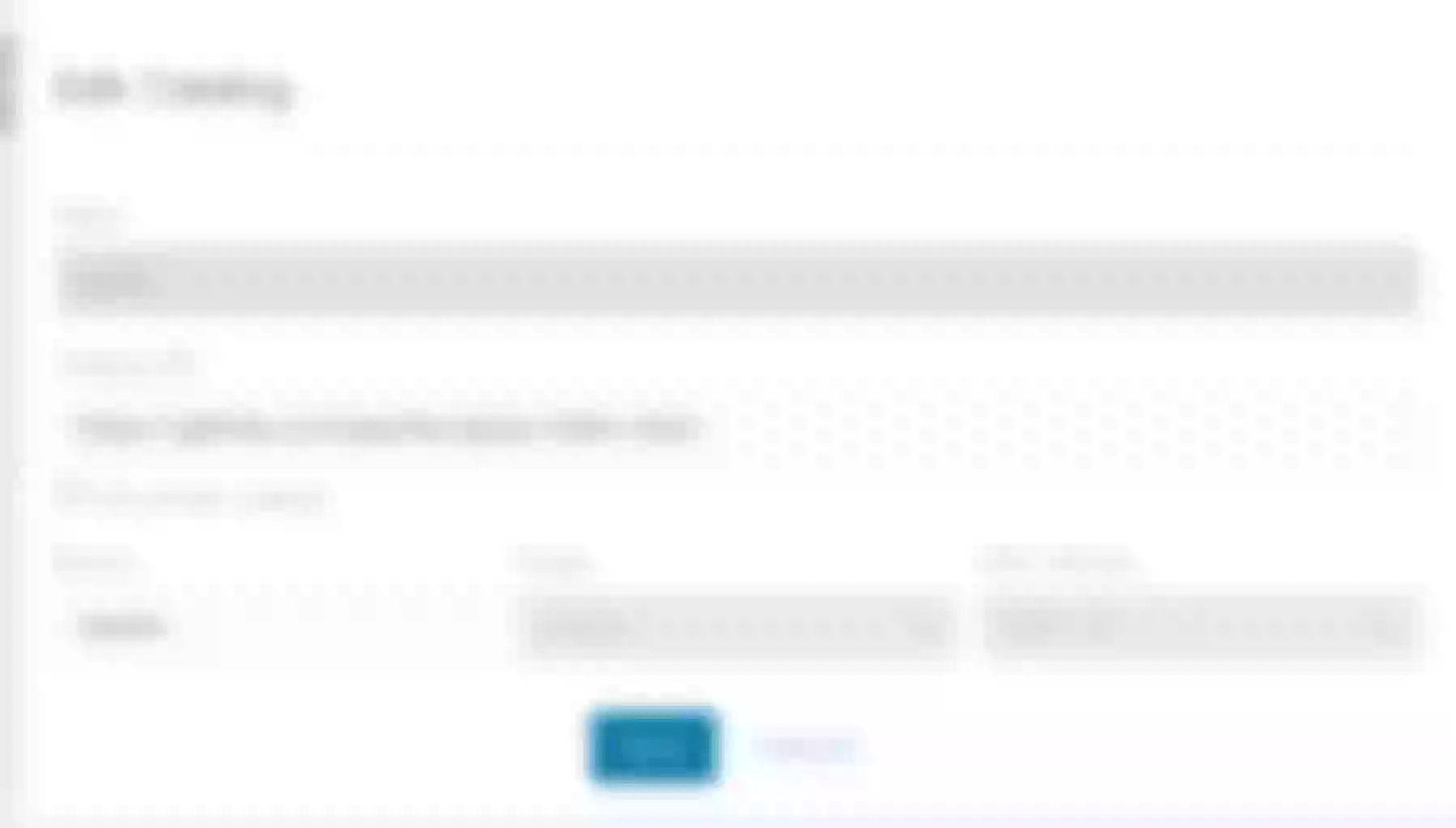
Click “Edit Catalog”, enter https://github.com/apache/apisix-helm-chart in “Catalog URL” to add the Helm repository for Apache APISIX in Rancher.
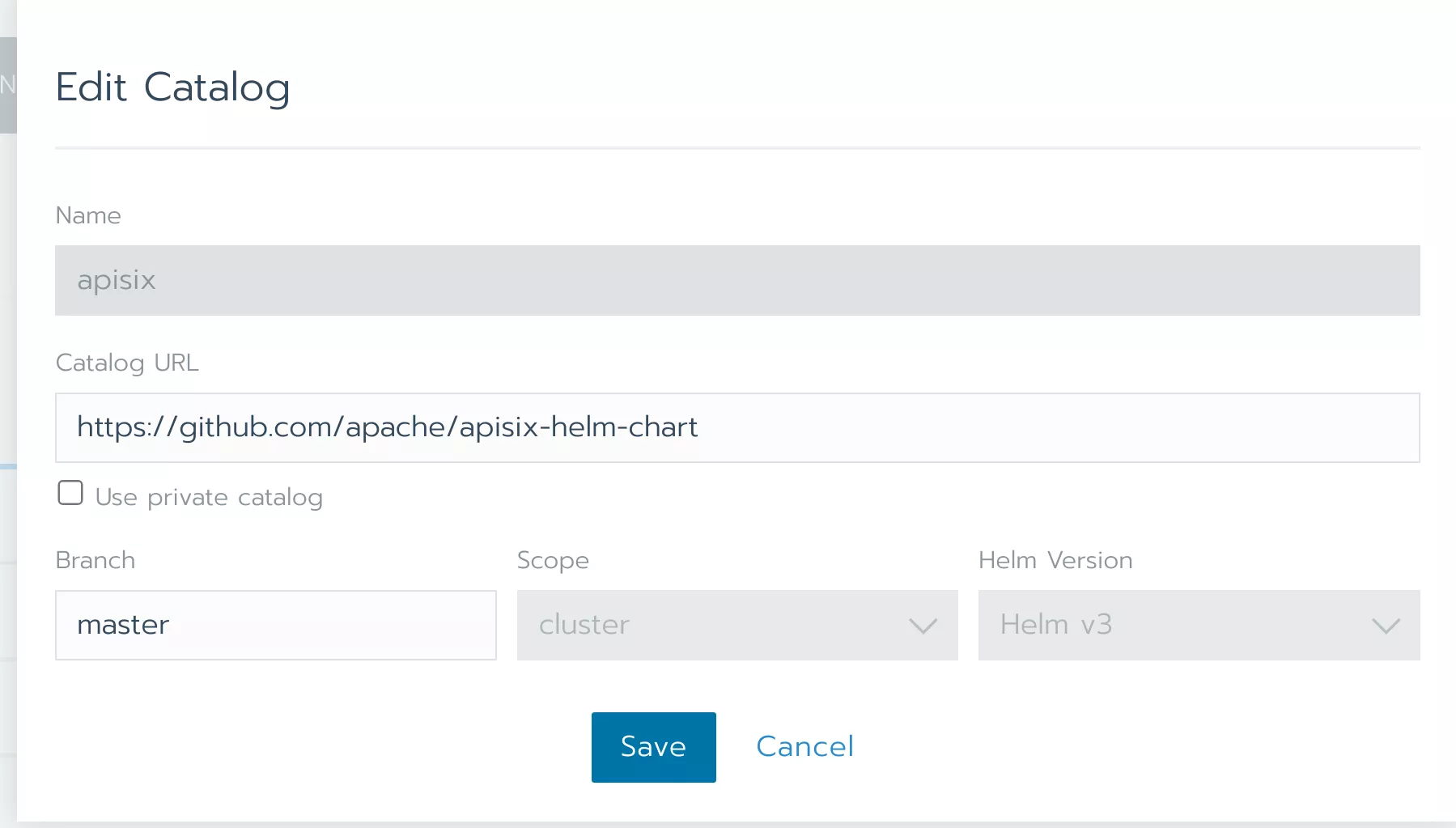
Click “Save” to save the changes.
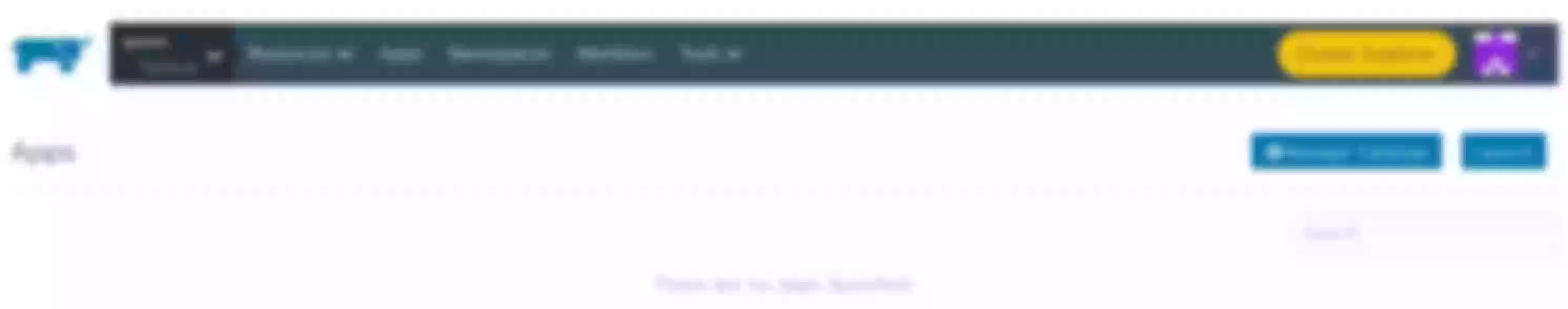
Select the Apps page, select Launch to see the Apache APISIX repository information. Here we can directly select “apisix” to deploy Apache APISIX.
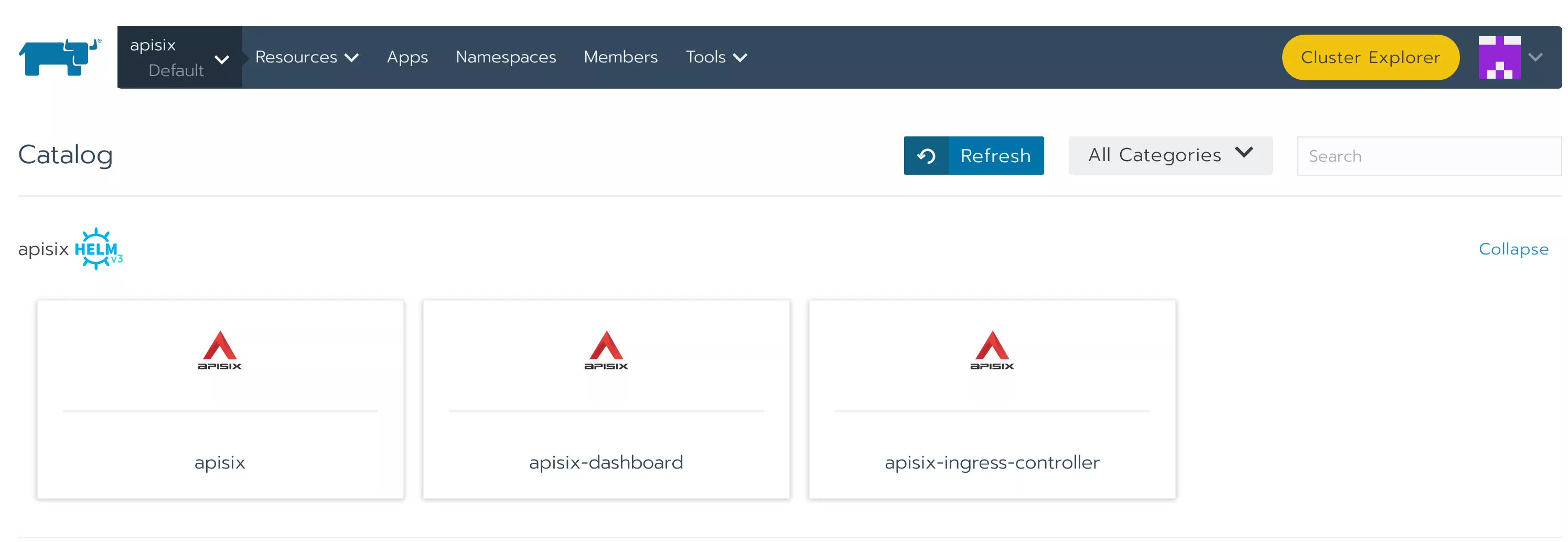
Since we want to deploy APISIX Ingress controller at the same time, fill in the ingress-controller.enabled=true in the Answers at the bottom. Then click 'Save" to complete the deployment.
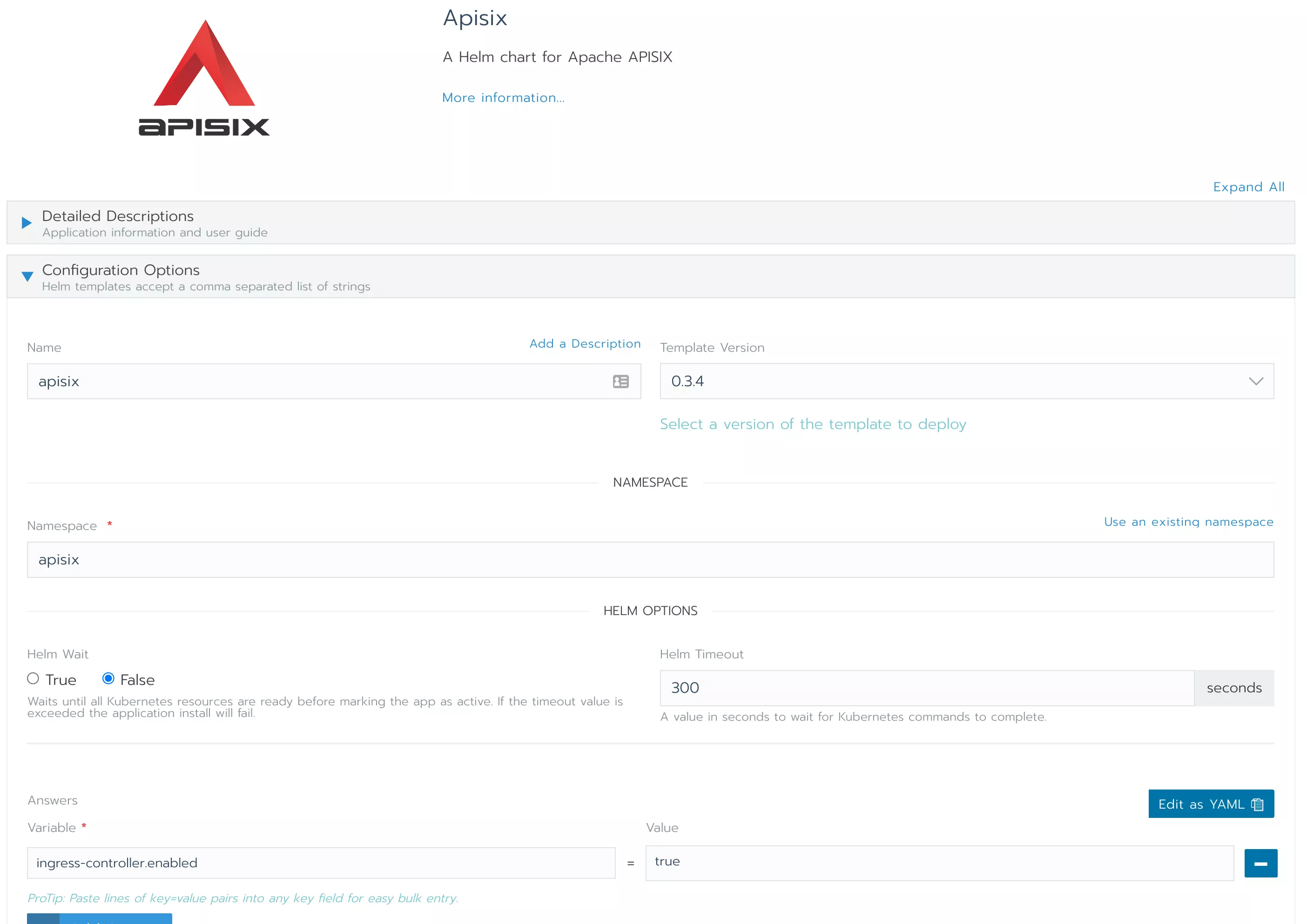
Wait a few moments for the deployment to complete.
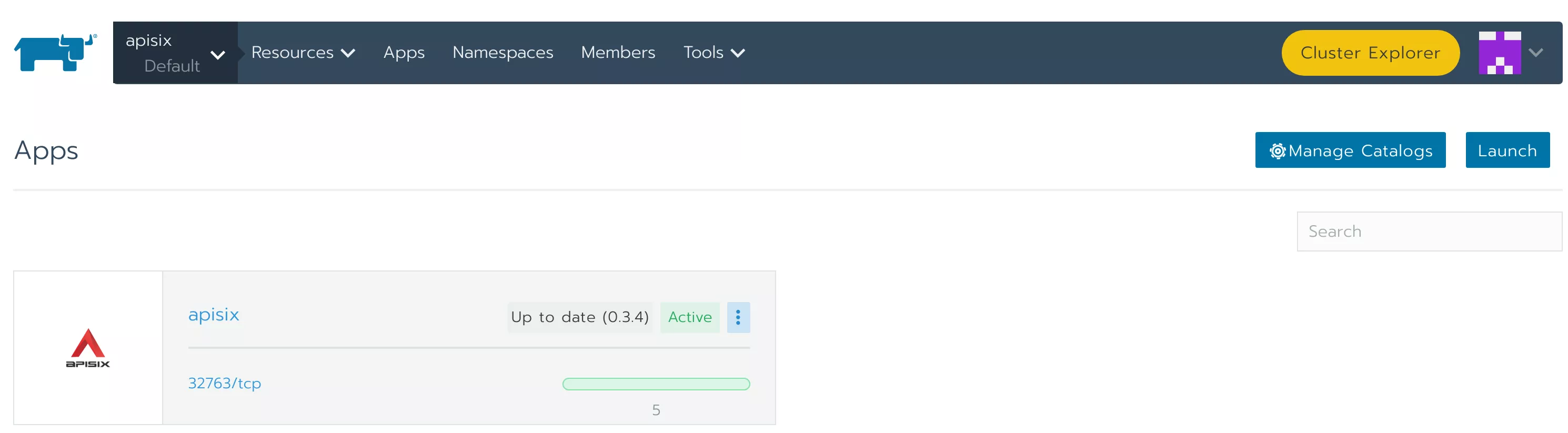
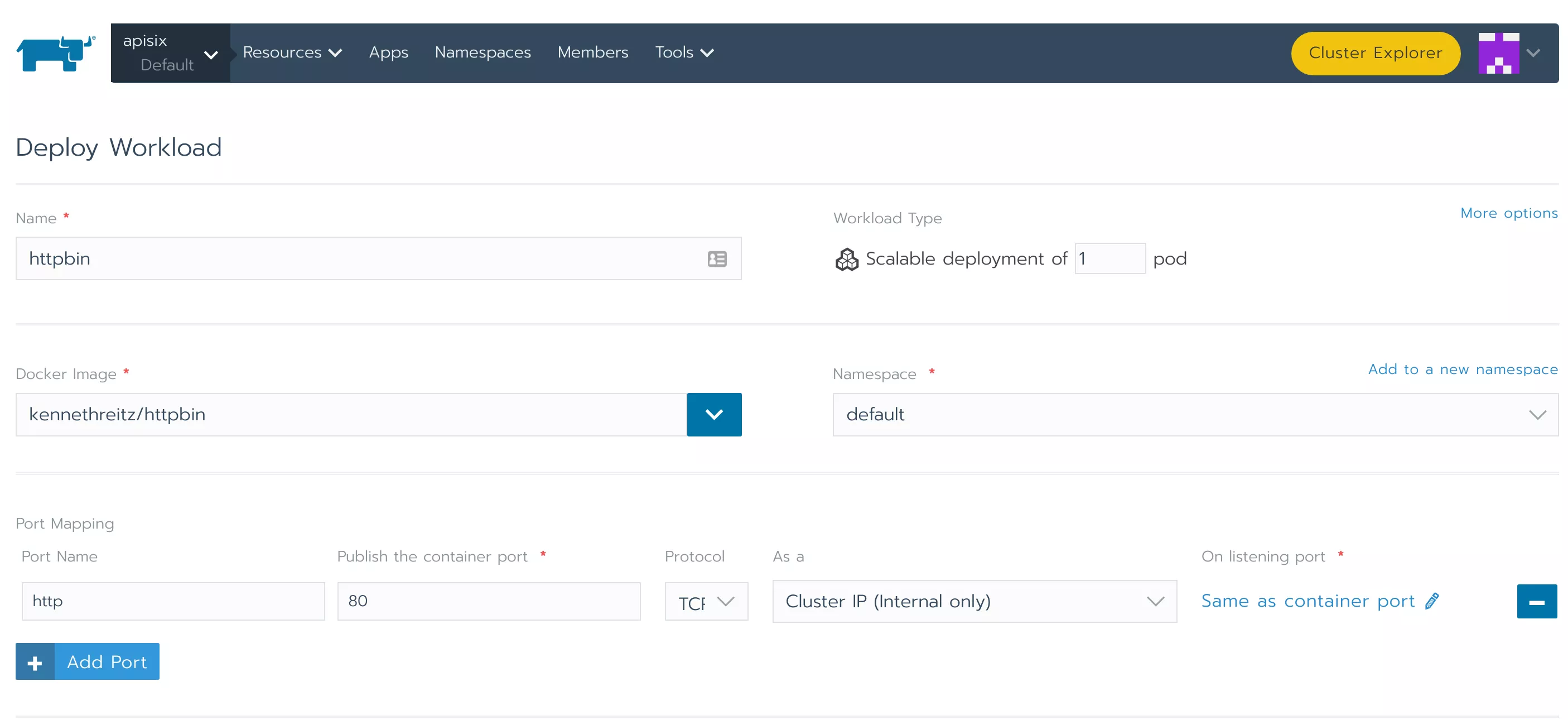
Step 2: Deploy an Example Project
We use kennethreitz/httpbin as a sample project for demonstration purpose. The deployment is also done directly in Rancher.
Step 3: Use Apache APISIX as an API Gateway to Proxy Services
First, We demonstrate how to use Apache APISIX as a gateway to proxy services in a Kubernetes cluster.
root@apisix:~$ kubectl -n apisix exec -it `kubectl -n apisix get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix -o name` -- bash
bash-5.1# curl httpbin.default/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.default",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.76.1"
},
"origin": "10.244.3.3",
"url": "http://httpbin.default/get"
}
You can see that the sample project can be accessed normally from within the Apache APISIX Pod. Next, we use Apache APISIX to proxy the sample project.
Here we use curl to call the admin interface of Apache APISIX to create a route. All requests with a host header of httpbin.org are forwarded to the actual application service httpbin.default:80.
bash-5.1# curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1" -H "X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1" -X PUT -d '
{
"uri": "/*",
"host": "httpbin.org",
"upstream": {
"type": "roundrobin",
"nodes": {
"httpbin.default:80": 1
}
}
}'
{"action":"set","node":{"value":{"uri":"\/*","create_time":1623834078,"update_time":1623834078,"priority":0,"upstream":{"type":"roundrobin","hash_on":"vars","pass_host":"pass","nodes":{"httpbin.default:80":1},"scheme":"http"},"id":"1","status":1,"host":"httpbin.org"},"key":"\/apisix\/routes\/1"}}
You will get an output similar to the above code block. Next, verify that the proxy is successful.
bash-5.1# curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/get -H "HOST: httpbin.org"
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.76.1",
"X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin.org"
},
"origin": "127.0.0.1",
"url": "http://httpbin.org/get"
}
The above output shows that the sample project traffic has been proxied through Apache APISIX. Next, let’s try accessing the sample project from outside the cluster via Apache APISIX.
root@apisix:~$ kubectl -n apisix get svc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
apisix-admin ClusterIP 10.96.142.88 <none> 9180/TCP 51m
apisix-gateway NodePort 10.96.158.192 <none> 80:32763/TCP 51m
When deployed using Helm chart, the Apache APISIX port is exposed by default as a NodePort. We use the Node IP + NodePort port for access testing.
root@apisix:~$ curl http://172.18.0.2:32763/get -H "HOST: httpbin.org"
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.58.0",
"X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin.org"
},
"origin": "10.244.3.1",
"url": "http://httpbin.org/get"
}
As you can see, Apache APISIX is able to proxy services within a Kubernetes cluster outside the cluster.
Step 4: Use Apache APISIX Ingress Controller Proxy Service
We can add Ingress directly to Rancher and the Apache APISIX Ingress controller will automatically synchronize the routing rules to Apache APISIX to complete the proxy for the service.
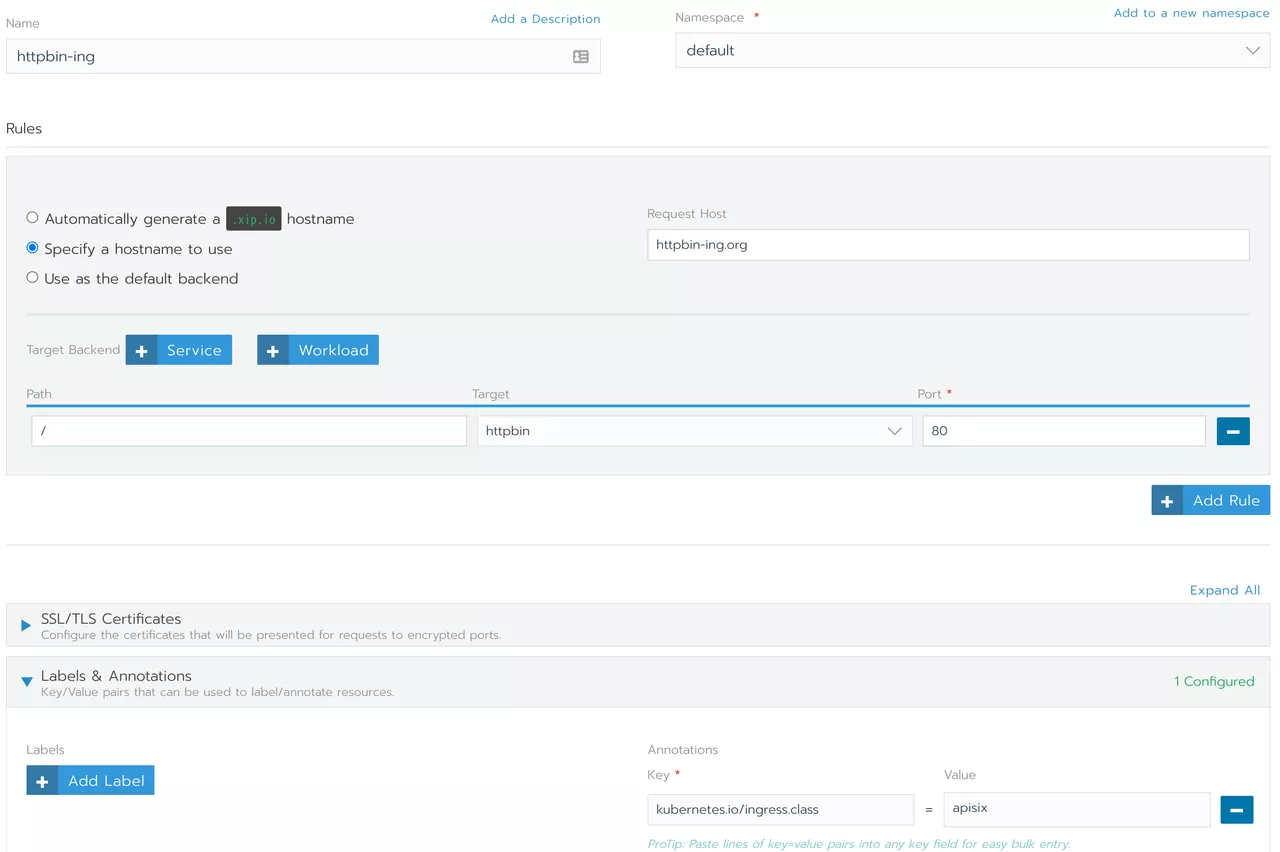
Note in the bottom right corner, we have added the annotation configuration kubernetes.io/ingress.class: apisix to support multiple ingress-controller scenarios in the cluster.
After saving, you can see the following screen.
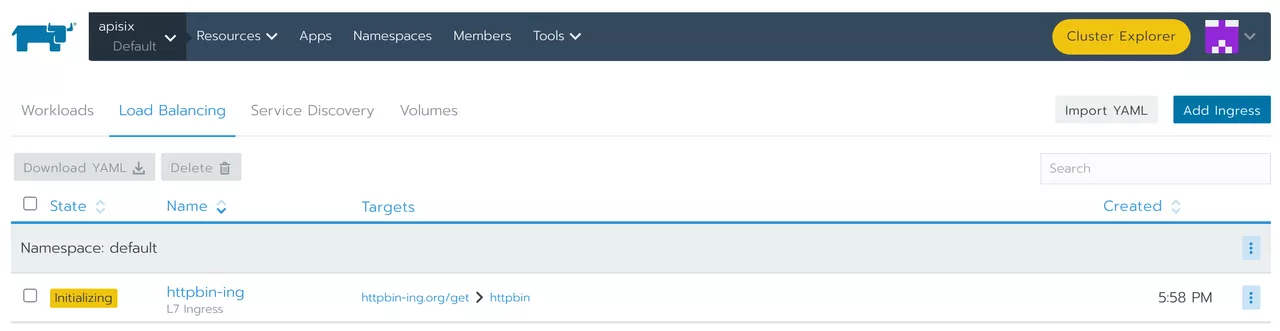
Test if the proxy is successful under the terminal:
root@apisix:~$ curl http://172.18.0.2:32763/get -H "HOST: httpbin-ing.org"
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin-ing.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.58.0",
"X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin-ing.org"
},
"origin": "10.244.3.1",
"url": "http://httpbin-ing.org/get"
}
You can see that it is also proxied properly.
In addition, the Apache APISIX Ingress controller extends Kubernetes by way of CRD, and you can also expose services in Kubernetes to the public by publishing custom resources like ApisixRoute.
Conclusion
You can deploy Apache APISIX and APISIX Ingress controller directly in Rancher using the official Apache APISIX Helm repository. And Apache APISIX can be used as a gateway or as a data plane for the APISIX Ingress controller to carry business traffic.
Future Plans
The Rancher community has partnered with Apache APISIX community. You will be able to find Apache APISIX directly in Rancher’s own app store in the future, eliminating the need to manually add Helm repositories.