Apache APISIX now supports writing plugins in Java! You can now write plugins in a programming language you are familiar with.
Introduction
Why Apache APISIX Supports Writing Plugins in Multiple Programming Languages?
Apache APISIX has been supporting customized plugins since the day it was born. But it only supported plugins written in Lua. As a result, developers need to have Lua and OpenResty-related development skills to actually write their own plugins. However, Lua and OpenResty are relatively less popular languages with fewer developers compared to Java and Go. Besides, learning Lua and OpenResty from scratch requires a lot of time and effort.
During technological selection, the most important consideration for the development team is whether the chosen product matches the team's technology stack. The niche technology stack limits Apache APISIX to become the first choice of API Gateway product in many scenarios.
Now, Apache APISIX supports multi-language development plugins. More importantly, the development ecosystem where the language is supported, so users can use their familiar technology stack to develop Apache APISIX. With Apache APISIX supporting plugins written in Java, for example, users can not only write plugins in Java but also integrate into the Spring Cloud ecosystem and use a wide range of technical components within the ecosystem.
Multiple Programming Languages Architecture Diagram
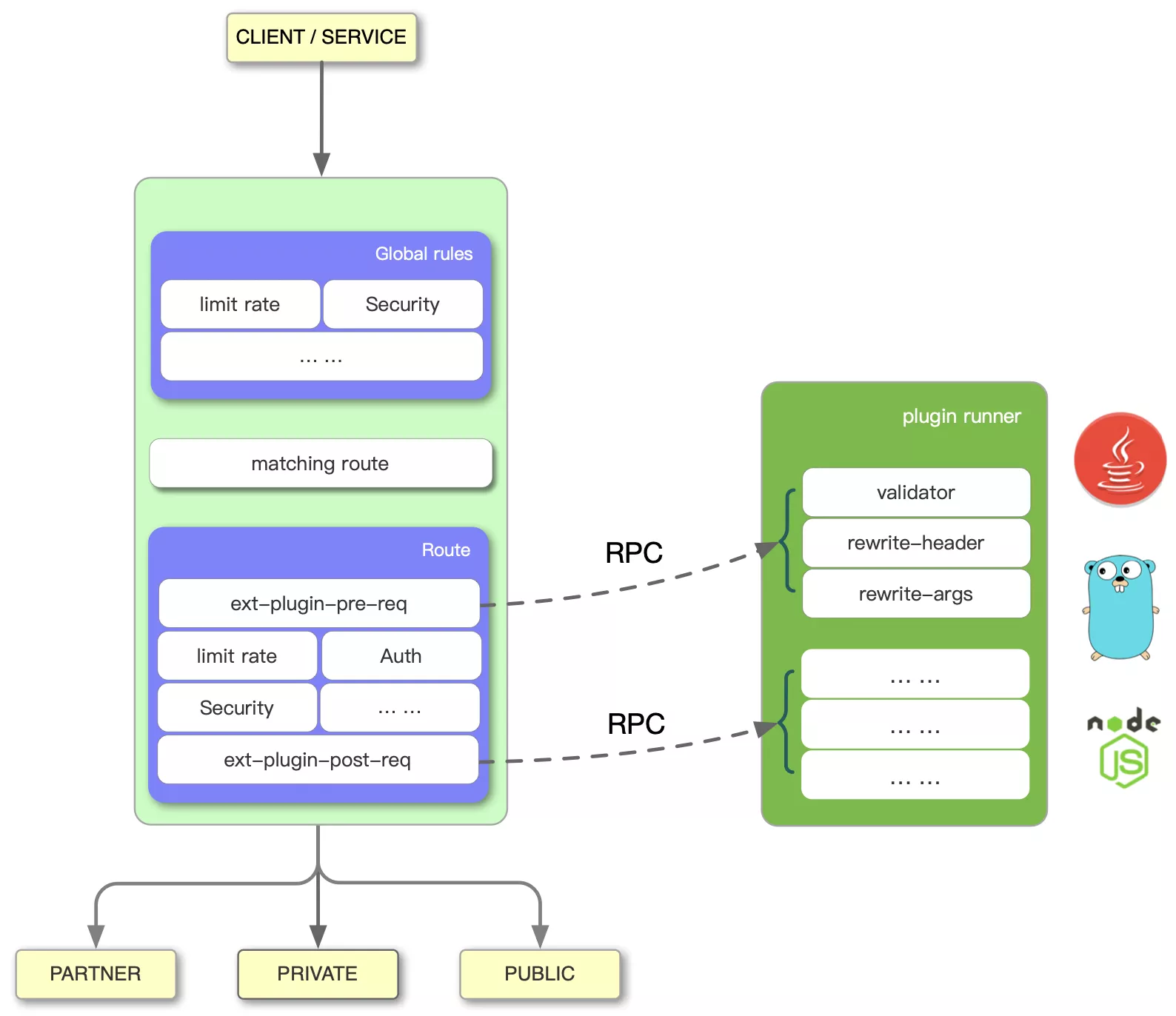
The left side of the diagram shows the workflow of Apache APISIX. The right side of the diagram is the plugin runner, which is a generic term for projects with multiple programming languages support. The apisix-java-plugin-runner is a plugin runner that supports the Java language.
When you configure a plugin runner in Apache APISIX, Apache APISIX starts a subprocess to run the plugin runner, which belongs to the same user as the Apache APISIX process. When we restart or reload Apache APISIX, the plugin runner will also be restarted.
If you configure the ext-plugin-* plugin for a given route, a request hitting that route will trigger Apache APISIX to perform an RPC call to the plugin runner via a Unix socket. The call is broken down into two phases:
- ext-plugin-pre-req: Before executing the Apache APISIX built-in plugin (Lua plugin)
- ext-plugin-post-req: After executing the Apache APISIX built-in plugin (Lua plugin)
Please configure the timing of the plugin runner execution as needed. The plugin runner processes the RPC call, creates a simulated request inside it, and then runs the multiple programming languages written a plugin and returns the result to Apache APISIX.
The order of execution of multiple programming languages plugins is defined in the ext-plugin-* plugin configuration entry. Like other plugins, they can be enabled and redefined on the fly.
Building Development Environment
First, you need to build the Apache APISIX runtime or development environment, please refer to Build Apache APISIX, and Build apisix-java-plugin-runner.
Note: Apache APISIX and apisix-java-plugin-runner need to be located on the same instance.
Enabling Debug Mode
Configuring Apache APISIX into Debug Mode
When Apache APISIX is configured into debug mode, it is allowed to run external plugins in a debugging manner. Add the following configuration to config.yaml to enable debug mode for Apache APISIX.
ext-plugin:
path_for_test: /tmp/runner.sock
The configuration above means that Apache APISIX acts as the client and listens to the Unix Domain Socket link located at /tmp/runner.sock.
Setting apisix-java-plugin-runner to Debug Mode
Before starting the Mainclass(org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.PluginRunnerApplication), you need to configure the user-level environment variables APISIX_LISTEN_ADDRESS=unix:/tmp/runner.sock and APISIX_CONF_EXPIRE_TIME=3600.
If you are using IDEA for development, the configured environment variables are shown below.
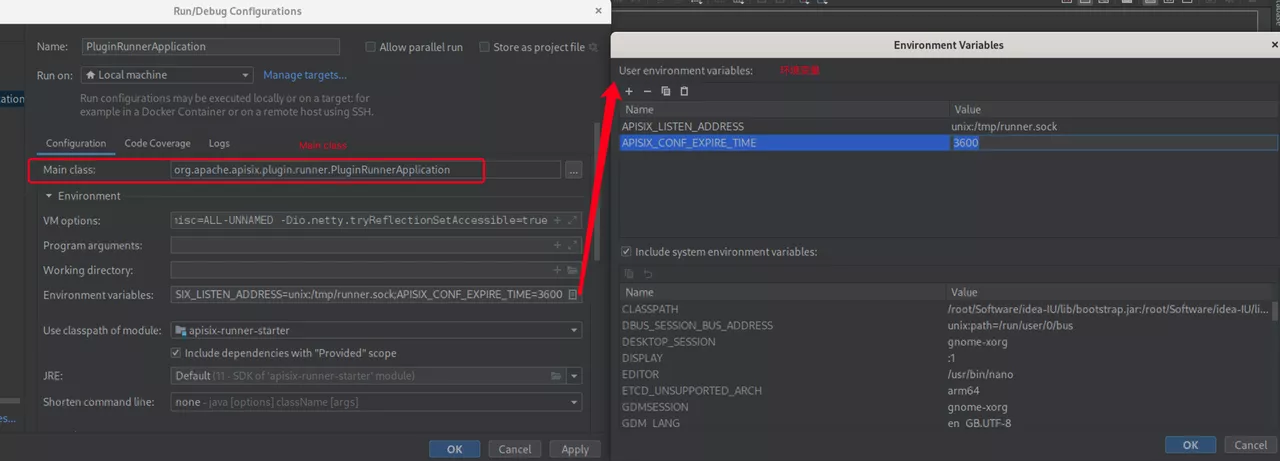
apisix-java-plugin-runner is equivalent to the server side and will actively create the /tmp/runner.sock file at startup and communicate with Apache APISIX on this file for Unix Domain Socket.
How to Develop a Java Plugin for Apache APISIX?
Scenario
Let's say we have a scenario like this: we need to verify the validity of the token in the request header. The way to verify the token is to carry the token as a parameter in the request and access the SSO fixed interface.
Configuring Apache APISIX
First, name the plugin TokenValidator, and then design the properties. In order to achieve dynamic configuration as far as possible, the properties are designed as follows.
{
"validate_header": "token",
"validate_url": "https://www.sso.foo.com/token/validate",
"rejected_code": "403"
}
Start Apache APISIX, then add a new route configuration specifying that the route requires a call to apisix-java-plugin-runner's TokenValidator plugin, as shown in the following example.
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
{
"uri":"/get",
"plugins":{
"ext-plugin-pre-req":{
"conf":[
{
"name":"TokenValidator",
"value":"{\"validate_header\":\"token\",\"validate_url\":\"https://www.sso.foo.com/token/validate\",\"rejected_code\":\"403\"}"
}
]
}
},
"upstream":{
"nodes":{
"httpbin.org:80":1
},
"type":"roundrobin"
}
}
Note that the properties of TokenValidator need to be escaped by json and configured as string type (the upstream address here is configured as httpbin.org to simplify the debugging process).
Developing a Java Plugin
Add TokenValidatr.java with the following initial code skeleton In the runner-plugin/src/main/java/org/apache/apisix/plugin/runner/filter directory.
package org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.filter;
import org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.HttpRequest;
import org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.HttpResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Component
public class TokenValidator implements PluginFilter {
@Override
public String name() {
return "TokenValidator";
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, PluginFilterChain chain) {
return chain.filter(request, response);
}
}
This plugin inherits the PluginFilter interface and overrides the name and the filter function. Rewrite the return value of name to be consistent with "name" in the route attribute of APISIX configuration earlier. The complete code is as follows.
package org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.filter;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.HttpRequest;
import org.apache.apisix.plugin.runner.HttpResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class TokenValidator implements PluginFilter {
@Override
public String name() {
return "TokenValidator";
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, PluginFilterChain chain) {
// parse `conf` to json
String configStr = request.getConfig(this);
Gson gson = new Gson();
Map<String, Object> conf = new HashMap<>();
conf = gson.fromJson(configStr, conf.getClass());
// get configuration parameters
String token = request.getHeader((String) conf.get("validate_header"));
String validate_url = (String) conf.get("validate_url");
boolean flag = validate(token, validate_url);
// token verification results
if (!flag) {
String rejected_code = (String) conf.get("rejected_code");
response.setStatusCode(Integer.parseInt(rejected_code));
return chain.filter(request, response);
}
return chain.filter(request, response);
}
private Boolean validate(String token, String validate_url) {
//TODO: improve the validation process
return true;
}
}
Testing the Plugin
The upstream service configured on Apache APISIX is httpbin.org, which allows you to access Apache APISIX, trigger the route, and have Apache APISIX call apisix-java-plugin-runner to execute the TokenValidator plugin and test the functionality of the Java plugin.
curl -H 'token: 123456' 127.0.0.1:9080/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "/",
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Token": "123456",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.71.1",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-60cb0424-02b5bf804cfeab5252392f96",
"X-Forwarded-Host": "127.0.0.1"
},
"origin": "127.0.0.1",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1/get"
}
Deploying the Plugin
After the development of the plugin is completed, the deployment operation can be found in referred to Deploying apisix-java-plugin-runner.